Let's start with history
As the internet became more popular in the early 2000s, people wanted to use more and more types of applications.
These applications needed to be able to handle a growing number of users and adapt to changing demands. To make this happen, the idea of "containerized" applications came about.
Containerized applications are like "boxes" that have everything an application needs to run inside, such as the code and necessary files.
In 2013, a tool called Docker was created to make creating these containerized applications easier. Because of this, more and more companies started using it to make their applications work better, be more efficient, and be easily portable.
But as the number of containerized applications grew, it became difficult to manage them all because it is easy to manage 2 containers manually but when it comes to 200 or maybe more containers it is painful to manage. To fix this, This led to the development of orchestration tools such as Kubernetes.
What is Kubernetes?
Kubernetes is a tool that helps manage and coordinate the many "boxes" or containers that make up an application. It's like a traffic controller for the containers, making sure they are running smoothly and efficiently, and that the right number of them are in the right place at the right time.
For example, imagine you have an online store that is running on multiple containers. Kubernetes can help you manage the containers by automatically scaling them up or down to handle changes in customer traffic, and monitoring their health to make sure they are running properly. If there is a problem with one of the containers, Kubernetes can also automatically replace it with a new one to keep the online store running smoothly.
In short, Kubernetes is a tool that helps to automate the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications, allowing developers to focus on developing their applications rather than managing the underlying infrastructure.
Kubernetes Architecture
In Kubernetes, you work with clusters.
A cluster refers to a set of machines (physical or virtual) that are used to run containerized applications. A Kubernetes cluster typically includes one or more master nodes (which we will understand in this blog) and multiple worker nodes.

In production, Kubernetes works with multiple hosts. This is known as a distributed deployment meaning the master node can host on a different machine and worker nodes can host on different Linux machine
This helps in a high level of scalability, availability, and fault tolerance (a higher level of availability in case one host goes down).
Master Node - and its components
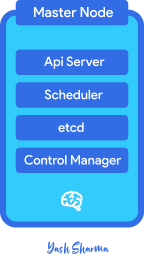
Think of the Kubernetes master node as a manager at a company. Just like a manager gives orders to the employees, the master node gives orders to the worker nodes. The master node is the "brain" of the Kubernetes cluster, it's in charge of making sure everything runs smoothly and coordinating the activities of the worker nodes.
The master node has several important parts that work together, like different departments in a company. In production kubernetes works with multiple master nodes
API Server
The API server is like the receptionist, it's the main point of contact for all requests and commands to the cluster.
etcd
The etcd is like the company's database, it stores important information about the cluster such as the state of the cluster and the deployed applications.
Controller Manager
The controller manager is like the supervisor, it makes sure everything is running as it should be and if not it takes actions to fix it.
Scheduler
Scheduler is like the HR, it decides where to place new pods based on factors such as resource usage of node and network topology. If no
Just like a manager communicates with the employees, the master node also communicates with the worker nodes to make sure everything is running as expected and takes corrective action if necessary, such as scaling up or down the number of replicas (copy of container in another node), monitoring resource usage, etc.
Overall, the master node acts as the control center for the Kubernetes cluster, coordinating the activities of worker nodes and ensuring that the desired state of the cluster is met, just like a manager in a company.
Worker Node - and its component

Worker nodes are the cluster service that actually does the work that's why they are called worker nodes.
To run containers inside node every node should have installed container runtime engine e.g Docker and kubelet which interacts with the node itself and with the container to assign manage resources.
Kubelet
Kubelet is an agent that runs on every worker node in a Kubernetes cluster. It is responsible for ensuring that containers are running as expected on the node and it communicates with the Kubernetes master node to receive instructions on how to run and manage the containers.
It also reports to the master node about node health.
Pods
Pod is the smallest unit in kubernet environment. Think like it is a runtime for container or a top layer for container, the reason to have this is to abstract container so that client should only interact with kubernetes layer not directly work with Docker or any container runtime technology.
It is best practice to run only one application container inside a pod, but you can run multiple application containers inside of it.
A worker node can have mutiple pods.
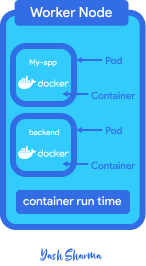
Container Runtime
Containers are going to be run inside of pods so they need to have a runtime evironment to run them. Whenever new worker node created first thing that happens inside node is installing runtime environment for containers. In our case we used Docker but it can also be any container runtime technology.
Kube-Proxy
Kube Proxy is a service that also need to be installed in every node. This help containers to make connection and communicate with each other by assigning them the IP address.
It also prevents network overhead by defined set of rules (kind of advance load balancer)
In short Kubelet and Kube-Proxy should install in every worker node independent of container runtime
Conclusion
Kubernetes is a powerful and flexible platform for managing containerized applications. In practice it is use for big applications with thousand of users
It helps organisations to scale their application fast and secure which help them to focus on there product. After it's official launch it is widely adopted by so many organisation.
Kubernetes is open-source and comes under in CNCF community checkout here
Greetings
💖 Thanks for reading in next blog we will cover how you can use kubernetes
For short updates you can chekout my Twitter - Yash Sharma